
drive into the future with the 2025 subaru forester...
October 14, 2025
10:53 am

need a new car? rent to own cars no credit check ...
October 14, 2025
10:57 am
Scientists Uncover How Plants Twist Molecules Into Powerful Anti-Cancer Compound
October 14, 2025
11:07

In a breakthrough that could revolutionize natural drug discovery, researchers have finally decoded how certain tropical plants produce mitraphylline, a rare, plant-based molecule known for its anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties.
The discovery, led by scientists at UBC Okanagan in collaboration with the University of Florida, reveals how two plant enzymes work together to create the compound’s unique three-dimensional “twisted” molecular structure, a feature that gives it potent biological activity.
Mitraphylline belongs to a class of molecules called spirooxindole alkaloids, complex organic compounds prized for their intricate shapes and pharmacological potential.
Recent Posts

want an suv with easy access and comfort for seniors? here’s how to get it!...
October 14, 2025
10:50 am

explore surprisingly affordable luxury ram 1500...
October 14, 2025
10:50 am

explore the 2025 jeep compas: adventure awaits!...
October 14, 2025
11:01 am

celebrate the holidays in a new hyundai palisade...
October 14, 2025
10:39 am
These compounds occur naturally in trace amounts in certain members of the coffee family, particularly tropical trees like Mitragyna speciosa (kratom) and Uncaria tomentosa (cat’s claw).
Despite their potential in cancer treatment and immune modulation, their scarcity in nature has long made them difficult to study and produce in useful quantities.
“This is similar to finding the missing links in an assembly line,” said Dr. Dang, UBC Okanagan’s Principal’s Research Chair in Natural Products Biotechnology. “It answers a long-standing question about how nature builds these complex molecules and gives us a new way to replicate that process.”
Recent Posts
 2025 Jeep Wrangler Price One Might Not Want to Miss!
2025 Jeep Wrangler Price One Might Not Want to Miss!2025 jeep wrangler price one might not want to miss!...
October 14, 2025
10:45 am
 Drive into the Future with the 2025 Subaru Forester
Drive into the Future with the 2025 Subaru Foresterdrive into the future with the 2025 subaru forester...
October 14, 2025
10:55 am
 Need a new Car? Rent To Own Cars No Credit Check
Need a new Car? Rent To Own Cars No Credit Checkneed a new car? rent to own cars no credit check ...
October 14, 2025
10:50 am
 Want an SUV with Easy Access and Comfort for Seniors? Here’s How to Get It!
Want an SUV with Easy Access and Comfort for Seniors? Here’s How to Get It!want an suv with easy access and comfort for seniors? here’s how to get it!...
October 14, 2025
11:06 am
The team discovered that plants use two specialized enzymes in tandem:
This “molecular origami”—a process of folding and twisting chemical rings- is what gives mitraphylline its distinctive spiro-shaped architecture.
Understanding how plants perform this twist at the enzymatic level has long been a “black box” for scientists. Now, for the first time, researchers can replicate the entire process in a lab, opening doors to scalable production.
Recent Posts

explore surprisingly affordable luxury ram 1500...
October 14, 2025
10:42 am

explore the 2025 jeep compas: adventure awaits!...
October 14, 2025
11:05 am

celebrate the holidays in a new hyundai palisade...
October 14, 2025
10:58 am

2025 jeep wrangler price one might not want to miss!...
October 14, 2025
11:05 am
By decoding and duplicating the biosynthetic pathway, researchers can now engineer mitraphylline artificially, without depending on rare plants or slow extraction methods.
This offers three major benefits:
In early studies, mitraphylline has shown promise in inhibiting tumor growth and modulating immune responses, though it remains under preclinical investigation. Replicating it synthetically could streamline testing and lead to next-generation plant-inspired cancer therapies.
Recent Posts

drive into the future with the 2025 subaru forester...
October 14, 2025
10:47 am

need a new car? rent to own cars no credit check ...
October 14, 2025
10:37 am

want an suv with easy access and comfort for seniors? here’s how to get it!...
October 14, 2025
10:45 am

explore surprisingly affordable luxury ram 1500...
October 14, 2025
10:40 am
The research team believes the breakthrough could have far-reaching effects beyond mitraphylline itself.
“By uncovering how plants use enzymes to twist molecules into new forms, we’ve opened a blueprint that can apply to many other bioactive compounds,” said Dr. Dang. “It’s a step toward a green drug revolution, where sustainable biotechnology replaces costly chemical synthesis.”
Experts in natural product chemistry note that this method could help reimagine drug development pipelines. Instead of extracting microgram quantities from endangered plants, scientists could now engineer microbes or plants to mass-produce these rare molecules safely and efficiently.
Recent Posts

explore the 2025 jeep compas: adventure awaits!...
October 14, 2025
10:55 am

celebrate the holidays in a new hyundai palisade...
October 14, 2025
11:05 am

2025 jeep wrangler price one might not want to miss!...
October 14, 2025
10:43 am

drive into the future with the 2025 subaru forester...
October 14, 2025
10:51 am
This discovery highlights how biotechnology is bridging the gap between nature and medicine. Many of today’s top pharmaceuticals, from aspirin to paclitaxel (Taxol) — originated from plants. But natural scarcity has always limited large-scale access.
Now, by mapping the enzymatic “assembly lines” behind these molecules, researchers can sustainably reproduce nature’s chemistry, a major stride toward eco-friendly drug innovation.
The next phase involves using synthetic biology and metabolic engineering to scale production and test mitraphylline’s effects in advanced preclinical cancer models.
If successful, the method could extend to other spirooxindole alkaloids with therapeutic potential, helping scientists explore an entire family of complex natural compounds previously deemed too rare to study in depth.
Recent Posts

If 2025 felt like a buildup year, 2026 is shaping up to be the payoff. Some of the most influential studios in the world—Rockstar Games, Capcom, Insomniac Games, IO Interactive, and Microsoft—are lining up releases...
December 15, 2025
1:54 pm

need a new car? rent to own cars no credit check ...
December 15, 2025
1:48 pm
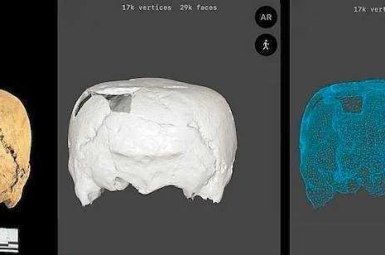
TL;DR Archaeologists in Mexico have uncovered a 1,400-year-old skull shaped like a cube—an unprecedented find in the region of Tamaulipas. The skull belonged to a man from the Classic period, and its shape was intentionally...
December 15, 2025
12:34 pm

want an suv with easy access and comfort for seniors? here’s how to get it!...
December 15, 2025
12:31 pm

The last meal tradition on death row has long raised questions about justice, ritual, and public spectacle. This week, that debate reignited after Georgia inmate Stacey Humphreys, who is scheduled for execution by lethal injection,...
December 15, 2025
7:23 am

explore surprisingly affordable luxury ram 1500...
December 15, 2025
7:14 am

The Hollywood director convicted of scamming Netflix out of $11 million is at the center of a case that’s forcing the entertainment industry to reexamine how studios fund ambitious creative projects and what happens when...
December 15, 2025
7:02 am

explore the 2025 jeep compas: adventure awaits!...
December 15, 2025
6:49 am

Newly released photographs from Jeffrey Epstein’s estate have brought some of the world’s most recognizable names back into public focus. Democratic lawmakers on the House Oversight Committee have published nearly 100 images obtained through subpoenas,...
December 15, 2025
6:49 am

celebrate the holidays in a new hyundai palisade...
December 15, 2025
6:26 am

TL;DR: Turkey’s Konya Plain is seeing a surge in massive sinkholes—some more than 100 feet wide and hundreds of feet deep. Nearly 700 have formed due to groundwater depletion, drought, and climate change. Farmers are...
December 15, 2025
6:44 am

2025 jeep wrangler price one might not want to miss!...
December 15, 2025
6:36 am